As the world increasingly turns to sustainable agricultural practices to address the challenges of climate change, soil degradation, and food security, bio fertilizers have emerged as a vital component in promoting healthy and productive soils. Bio fertilizers, which are derived from natural sources such as microorganisms, organic matter, and plant residues, offer a sustainable alternative to chemical fertilizers. Establishing a bio fertilizer plant is a significant investment, and understanding the project cost is crucial for ensuring its financial viability and long-term success. This article delves into the various cost components and factors influencing the overall expenditure of a bio fertilizer plant project.
The Importance of Bio Fertilizers
Bio fertilizers play a crucial role in sustainable agriculture by enhancing soil fertility, promoting plant growth, and improving crop yields. Unlike chemical fertilizers, bio fertilizers are environmentally friendly and contribute to the long-term health of the soil. They work by:
- Fixing Atmospheric Nitrogen: Certain microorganisms in bio fertilizers can fix atmospheric nitrogen, making it available to plants and reducing the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers.
- Solubilizing Phosphates: Bio fertilizers can solubilize phosphates, making them more accessible to plants and improving phosphorus uptake.
- Decomposing Organic Matter: Bio fertilizers help decompose organic matter, releasing essential nutrients and improving soil structure.
- Enhancing Soil Microbial Activity: Bio fertilizers promote the growth of beneficial soil microorganisms, enhancing soil health and resilience.
Key Cost Components of a Bio Fertilizer Plant Project
The cost of establishing a bio fertilizer plant can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the scale of the project, location, and technology used. The key bio fertilizer plant project cost components can be broadly categorized as follows:
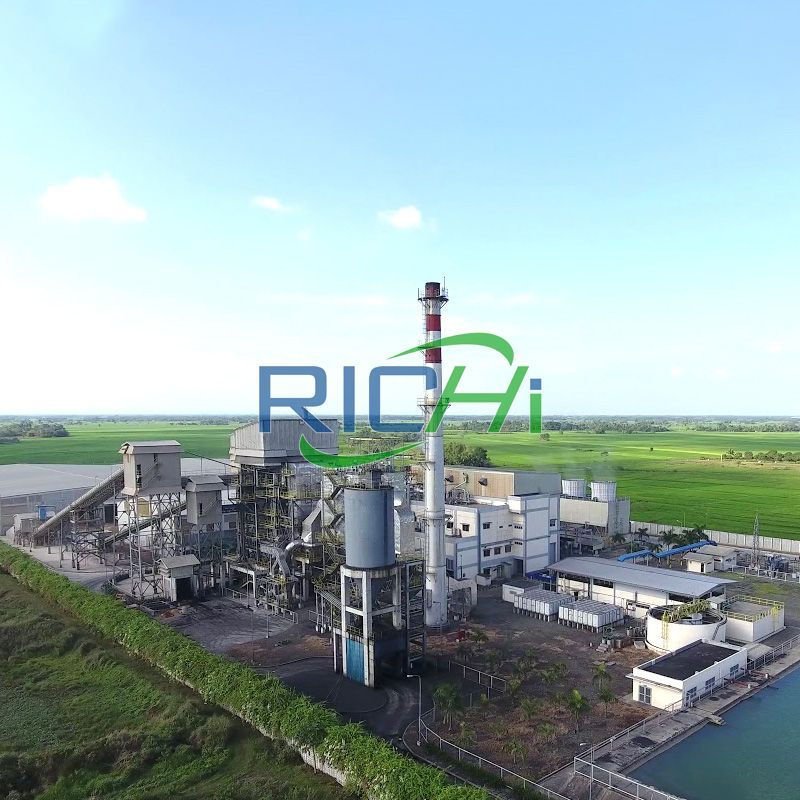
- Land and Site Development: The cost of acquiring land and preparing the site for construction is a significant component of the overall project cost. This includes expenses related to land acquisition, site clearing, grading, and infrastructure development such as access roads, utilities, and drainage systems.
- Plant Design and Engineering: The design and engineering phase involves creating detailed plans and specifications for the bio fertilizer plant. This includes architectural and engineering services, feasibility studies, environmental impact assessments, and obtaining necessary permits and approvals.
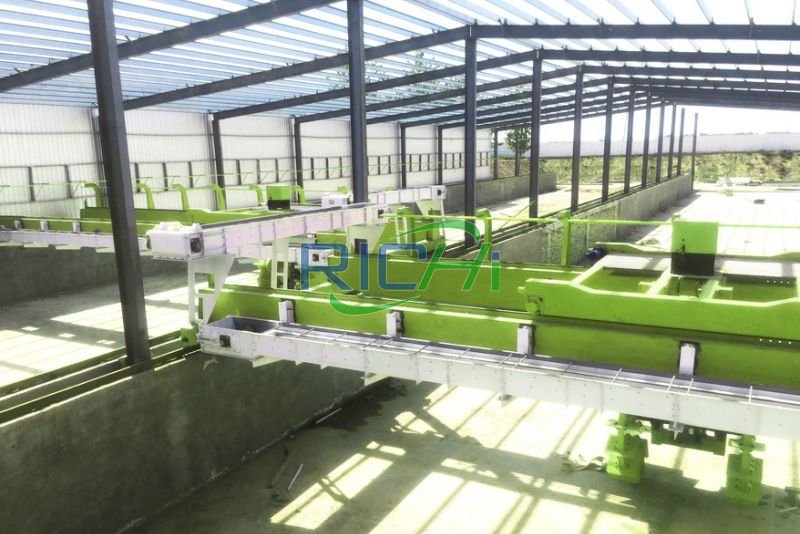
- Construction and Civil Works: The construction phase encompasses the building of the plant’s physical infrastructure, including production facilities, storage areas, administrative offices, and utility installations. This component also covers the cost of materials, labor, and construction equipment.
- Machinery and Equipment: The cost of purchasing and installing machinery and equipment is a major component of the project cost. This includes equipment for raw material handling, fermentation, mixing, granulation, drying, cooling, and packaging. The choice of technology and equipment can significantly impact the overall cost and efficiency of the plant.
- Raw Materials and Inputs: The cost of raw materials and inputs required for bio fertilizer production, such as organic matter, microorganisms, and additives, must be factored into the project cost. Ensuring a consistent and reliable supply of high-quality raw materials is crucial for the plant’s operation.
- Labor and Staffing: The cost of hiring and training personnel to operate and manage the bio fertilizer plant is an important consideration. This includes salaries, benefits, and training programs for skilled and unskilled workers, as well as administrative and management staff.
- Utilities and Energy: The cost of utilities and energy required to operate the plant, including electricity, water, and gas, must be accounted for. Implementing energy-efficient technologies and practices can help reduce operational costs.
- Quality Control and Testing: Ensuring the quality and efficacy of the bio fertilizer products requires investment in quality control and testing facilities. This includes laboratory equipment, testing kits, and personnel for conducting regular quality assessments.
- Marketing and Distribution: The cost of marketing and distributing the bio fertilizer products to end-users is an essential component of the project cost. This includes expenses related to branding, packaging, transportation, and establishing distribution networks.
- Contingency and Miscellaneous Costs: It is prudent to allocate a contingency budget to cover unforeseen expenses and cost overruns. Miscellaneous costs may include legal fees, insurance, and other administrative expenses.
Factors Influencing Bio Fertilizer Plant Project Cost
Several factors can influence the overall cost of a bio fertilizer plant project, including:
- Scale of Production: The scale of production, whether small, medium, or large, significantly impacts the project cost. Larger plants benefit from economies of scale but require higher initial investments.
- Location: The location of the plant affects land acquisition costs, availability of raw materials, labor costs, and access to markets. Proximity to raw material sources and target markets can reduce transportation costs and improve operational efficiency.
- Technology and Equipment: The choice of technology and equipment used in the production process can influence the cost and efficiency of the plant. Advanced and automated systems may have higher upfront costs but offer long-term benefits in terms of productivity and operational efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with local and national regulations, including environmental, health, and safety standards, can impact the project cost. Obtaining necessary permits and adhering to regulatory requirements may involve additional expenses.
- Financing and Investment: The availability of financing options, such as loans, grants, and subsidies, can affect the overall project cost. Interest rates, repayment terms, and equity contributions must be considered when planning the financial aspects of the project.
Related post: https://www.richipelletmachine.com/organic-fertilizer-production-plant-cost/
Cost Optimization Strategies
To ensure the financial viability and long-term success of a bio fertilizer plant project, it is essential to implement cost optimization strategies. These may include:
- Thorough Planning and Feasibility Studies: Conducting comprehensive planning and feasibility studies can help identify potential challenges and opportunities, enabling informed decision-making and cost-effective project execution.
- Efficient Resource Management: Implementing efficient resource management practices, such as optimizing raw material usage, reducing waste, and conserving energy, can help minimize operational costs.
- Leveraging Technology: Investing in advanced and automated technologies can improve production efficiency, reduce labor costs, and enhance product quality, leading to long-term cost savings.
- Strategic Partnerships: Forming strategic partnerships with suppliers, distributors, and other stakeholders can create synergies and leverage shared resources, reducing costs and risks.
- Accessing Financial Incentives: Exploring available financial incentives, such as government grants, subsidies, and tax credits, can help offset initial investment costs and improve project economics.
- Continuous Improvement: Implementing continuous improvement practices, such as regular maintenance, process optimization, and employee training, can enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime, contributing to cost savings.
Conclusion
Establishing a bio fertilizer pellet plant is a significant investment that requires careful planning, thorough analysis, and strategic decision-making. By understanding the various cost components and factors influencing the overall expenditure, investors and entrepreneurs can navigate the financial landscape and ensure the success of their bio fertilizer plant project.
As the global demand for sustainable agricultural practices continues to grow, bio fertilizers will play a crucial role in promoting soil health, enhancing crop productivity, and contributing to a more sustainable and resilient food system. With ongoing research, innovation, and strategic investments, the bio fertilizer industry is poised to drive the future of sustainable agriculture and environmental stewardship.