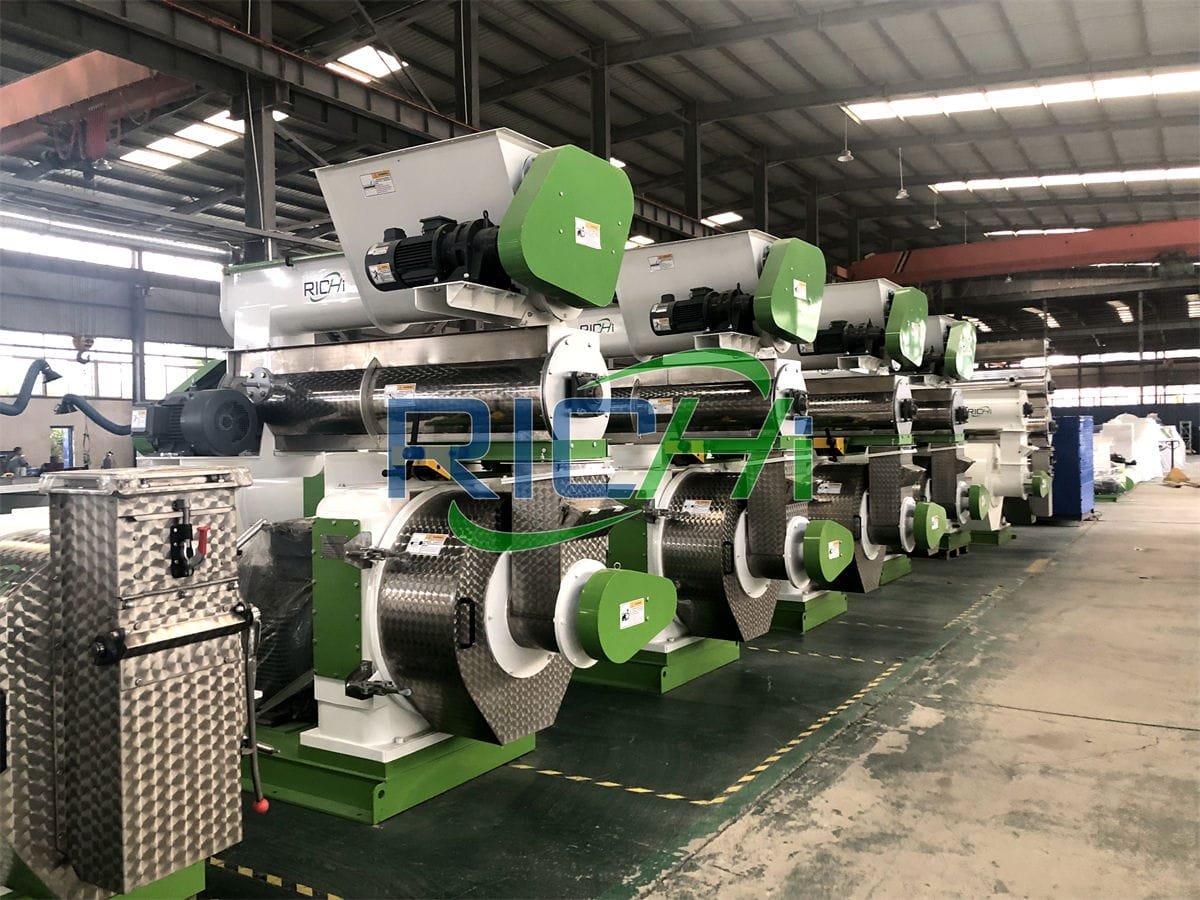
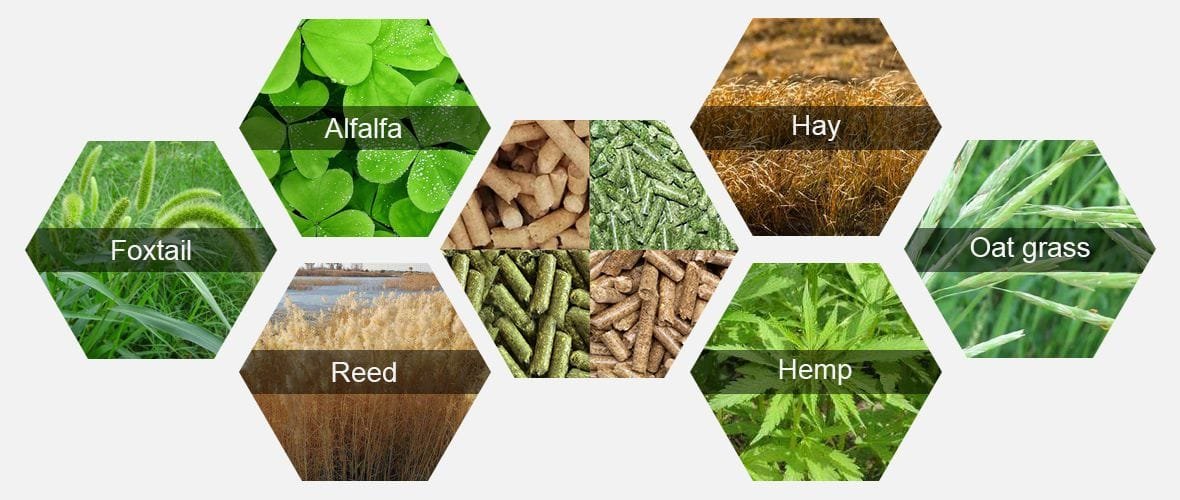
Livestock feed pellet machines are versatile tools designed to convert various feed ingredients into compact, digestible pellets. As the need for efficient and nutritious animal feed rises, many farmers and feed manufacturers are considering the production of silage pellets. This article explores whether livestock feed pellet machines can effectively process silage into pellets, the challenges involved, and the potential benefits of pelletizing silage.
Understanding Silage and Silage Pellets
Before examining the capabilities of livestock feed pellet machines, it’s essential to understand silage and the benefits of pelletizing it:
- Silage is fermented, high-moisture fodder typically made from grass crops such as corn, sorghum, or other cereals.
- Traditional silage is stored in silos or wrapped in plastic to maintain anaerobic conditions during fermentation.
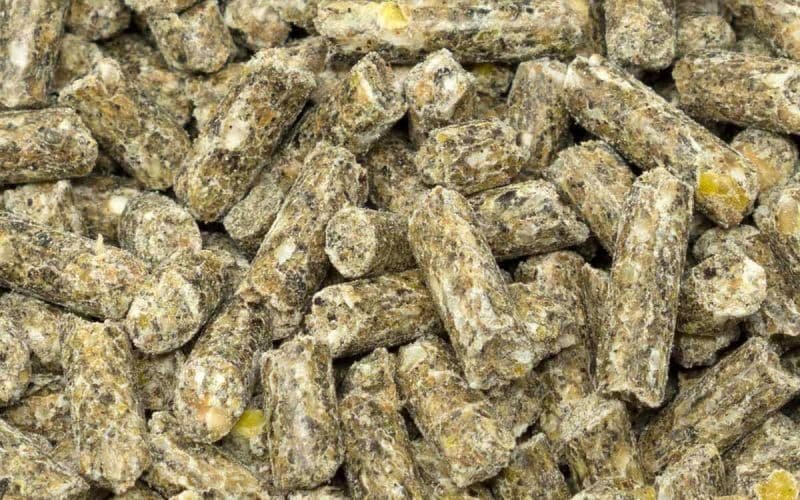
- Silage pellets are a compressed form of silage that can enhance storage, transportation, and feeding efficiency.
Challenges in Processing Silage with Livestock Feed Pellet Machines
While livestock feed pellet machines are adaptable, processing silage into pellets poses several unique challenges:
- Moisture Content: Traditional silage has a high moisture content (typically 60-70%), significantly exceeding the optimal moisture level for pelletizing (usually 15-18%). Excess moisture can cause clogging in the pellet die and lead to poor pellet formation.
- Fiber Length: Silage often contains long fibers that standard pellet machines may struggle to process effectively. Long fibers can prevent proper binding in the pellets, resulting in low durability.
- Nutrient Preservation: The heat generated during the pelletizing process may degrade some beneficial nutrients and bacteria present in silage.
- Fermentation Characteristics: The fermentation process that makes silage valuable might be disrupted during pelletizing, potentially altering its nutritional profile.
- Equipment Wear: The high moisture and acidity of silage can accelerate wear on pellet machine components.

Potential Solutions and Adaptations
Despite these challenges, livestock feed pellet machines can potentially process silage into pellets with proper adaptations and pre-processing:
- Pre-drying: Reducing moisture content before pelletizing can significantly enhance the process. This could involve field wilting or mechanical dewatering.
- Mixing with Dry Ingredients: Blending silage with drier feed ingredients can help achieve optimal moisture levels for pelletizing, resulting in a more balanced feed product.
- Chopping and Grinding: Utilizing specialized equipment to chop and grind silage before pelletizing can address issues related to long fibers, as finer particles bind more effectively.
- Die and Roller Modifications: Employing dies with larger hole diameters and shorter land lengths can improve processing of silage material. Adjusting roller pressure and speed can also accommodate the unique characteristics of silage.
- Temperature Control: Implementing precise temperature control during the pelletizing process can help preserve beneficial nutrients and bacteria. This may include cooler conditioning temperatures or shorter retention times in the pellet die.
- Corrosion-Resistant Materials: Using corrosion-resistant materials for critical components can mitigate wear caused by the acidity of silage.
Potential Benefits of Silage Pellets
If the challenges of processing silage with livestock feed pellet machines can be addressed, several potential benefits could arise from producing silage pellets:
- Improved Storage and Transportation: Pelletized silage occupies less space and is easier to transport than traditional silage. Pellets can also be stored longer without significant degradation.
- Reduced Waste: Silage pellets are less prone to spoilage and waste compared to traditional storage methods.
- Precise Feeding: Silage pellets allow for more accurate portioning and mixing with other feed ingredients.
- Versatility: Pelletized silage can be more easily incorporated into total mixed rations (TMR) or used as a standalone feed.
- Potential for Value-Added Products: Silage pellets could be fortified with additional nutrients or additives, creating premium feed products.
Case Studies and Research
Although the use of standard livestock feed pellet machines for silage pelletization is not widespread, some research and development efforts in this area have shown promise:
- A study at a European agricultural university demonstrated successful pelletization of silage after reducing its moisture content to around 25-30% and mixing it with dry ingredients.
- An agricultural equipment manufacturer in North America has developed a specialized “wet pellet” machine designed to handle materials with higher moisture content, including partially dried silage.
- Some innovative farmers have reported success in producing silage-based pellets by blending partially dried silage with dry hay or straw before pelletizing.
Considerations for Feed Mills and Farmers
For feed mills and farmers considering the production of silage pellets with livestock feed pellet machines, several factors should be taken into account:
- Equipment Investment: Additional pre-processing equipment, such as dryers or specialized choppers, may be necessary, along with potential modifications to existing pellet machines.
- Energy Costs: The drying process for high-moisture silage can be energy-intensive, impacting production costs.
- Product Testing: Extensive testing is necessary to ensure the nutritional quality and safety of silage pellets.
- Market Demand: Assessing the potential market for silage pellets in the region is crucial before investing in production capabilities.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that silage pellet production adheres to all relevant feed safety regulations is essential.
Conclusion
While standard livestock feed pellet machines face significant challenges in processing silage into pellets, proper adaptations and pre-processing may enable the production of silage-based pellets. The potential benefits of silage pelletization—such as improved storage, transportation, and feeding efficiency—make it a valuable area for further research and development.
For feed manufacturers and farmers interested in silage pelletization, a cautious approach involving thorough research, equipment testing, and product evaluation is recommended. Collaborating with agricultural engineers and nutritionists can help develop effective methods for producing high-quality silage pellets using modified livestock feed pellet machines. (Related post: cow feed pellet making machine cost)
As the demand for efficient and sustainable animal feed solutions continues to grow, innovations in processing methods, including the potential for silage pelletization, are likely to play an increasingly important role in the livestock feed industry. While challenges remain, the possibility of effectively pelletizing silage represents an exciting frontier in feed production technology.